Trigger pipelines by using the API (FREE ALL)
To trigger a pipeline for a specific branch or tag, you can use an API call to the pipeline triggers API endpoint.
When authenticating with the API, you can use:
- A pipeline trigger token to trigger a branch or tag pipeline.
- A CI/CD job token to trigger a multi-project pipeline.
Create a pipeline trigger token
You can trigger a pipeline for a branch or tag by generating a pipeline trigger token and using it to authenticate an API call. The token impersonates a user's project access and permissions.
Prerequisite:
- You must have at least the Maintainer role for the project.
To create a trigger token:
- On the left sidebar, at the top, select Search GitLab ({search}) to find your project.
- Select Settings > CI/CD.
- Expand Pipeline trigger tokens.
- Select Add new token
- Enter a description and select Create pipeline trigger token.
- You can view and copy the full token for all triggers you have created.
- You can only see the first 4 characters for tokens created by other project members.
WARNING:
It is a security risk to save tokens in plain text in public projects. Potential
attackers could use a trigger token exposed in the .gitlab-ci.yml file to impersonate
the user that created the token. Use masked CI/CD variables
to improve the security of trigger tokens.
Trigger a pipeline
After you create a pipeline trigger token, you can use it to trigger pipelines with a tool that can access the API, or a webhook.
Use cURL
You can use cURL to trigger pipelines with the pipeline trigger token API endpoint. For example:
-
Use a multiline cURL command:
curl --request POST \ --form token=<token> \ --form ref=<ref_name> \ "https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/projects/<project_id>/trigger/pipeline" -
Use cURL and pass the
<token>and<ref_name>in the query string:curl --request POST \ "https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/projects/<project_id>/trigger/pipeline?token=<token>&ref=<ref_name>"
In each example, replace:
- The URL with
https://gitlab.comor the URL of your instance. -
<token>with your trigger token. -
<ref_name>with a branch or tag name, likemain. -
<project_id>with your project ID, like123456. The project ID is displayed at the top of every project's landing page.
Use a CI/CD job
You can use a CI/CD job with a pipeline triggers token to trigger pipelines when another pipeline runs.
For example, to trigger a pipeline on the main branch of project-B when a tag
is created in project-A, add the following job to project A's .gitlab-ci.yml file:
trigger_pipeline:
stage: deploy
script:
- 'curl --fail --request POST --form token=$MY_TRIGGER_TOKEN --form ref=main "https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/projects/123456/trigger/pipeline"'
rules:
- if: $CI_COMMIT_TAG
environment: productionIn this example:
-
1234is the project ID forproject-B. The project ID is displayed at the top of every project's landing page. - The
rulescause the job to run every time a tag is added toproject-A. -
MY_TRIGGER_TOKENis a masked CI/CD variables that contains the trigger token.
Use a webhook
To trigger a pipeline from another project's webhook, use a webhook URL like the following for push and tag events:
https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/projects/<project_id>/ref/<ref_name>/trigger/pipeline?token=<token>Replace:
- The URL with
https://gitlab.comor the URL of your instance. -
<project_id>with your project ID, like123456. The project ID is displayed at the top of the project's landing page. -
<ref_name>with a branch or tag name, likemain. This value takes precedence over theref_namein the webhook payload. The payload'srefis the branch that fired the trigger in the source repository. You must URL-encode theref_nameif it contains slashes. -
<token>with your pipeline trigger token.
Access webhook payload
- Introduced in GitLab 13.9.
- Feature flag removed in GitLab 13.11.
If you trigger a pipeline by using a webhook, you can access the webhook payload with
the TRIGGER_PAYLOAD predefined CI/CD variable.
The payload is exposed as a file-type variable,
so you can access the data with cat $TRIGGER_PAYLOAD or a similar command.
Pass CI/CD variables in the API call
You can pass any number of CI/CD variables in the trigger API call. These variables have the highest precedence, and override all variables with the same name.
The parameter is of the form variables[key]=value, for example:
curl --request POST \
--form token=TOKEN \
--form ref=main \
--form variables[UPLOAD_TO_S3]="true" \
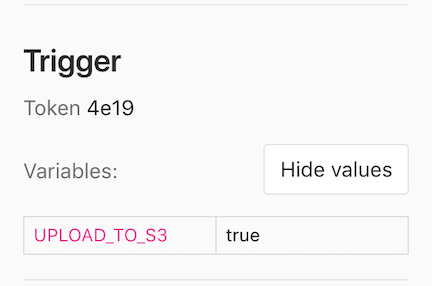
"https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/projects/123456/trigger/pipeline"CI/CD variables in triggered pipelines display on each job's page, but only users with the Owner and Maintainer role can view the values.
Revoke a pipeline trigger token
To revoke a pipeline trigger token:
- On the left sidebar, at the top, select Search GitLab ({search}) to find your project.
- Select Settings > CI/CD.
- Expand Pipeline triggers.
- To the left of the trigger token you want to revoke, select Revoke ({remove}).
A revoked trigger token cannot be added back.
Configure CI/CD jobs to run in triggered pipelines
To configure when to run jobs in triggered pipelines, you can:
- Use
ruleswith the$CI_PIPELINE_SOURCEpredefined CI/CD variable. - Use
only/exceptkeywords, thoughrulesis the preferred keyword.
$CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE value |
only/except keywords |
Trigger method |
|---|---|---|
trigger |
triggers |
In pipelines triggered with the pipeline triggers API by using a trigger token. |
pipeline |
pipelines |
In multi-project pipelines triggered with the pipeline triggers API by using the $CI_JOB_TOKEN, or by using the trigger keyword in the CI/CD configuration file. |
Additionally, the $CI_PIPELINE_TRIGGERED predefined CI/CD variable is set to true
in pipelines triggered with a pipeline trigger token.
See which pipeline trigger token was used
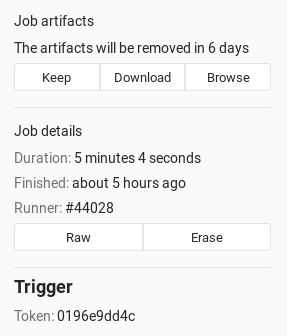
You can see which pipeline trigger token caused a job to run by visiting the single job page. A part of the trigger token displays on the right of the page, under the job details:
In pipelines triggered with a trigger token, jobs are labeled as triggered in
Build > Jobs.
Troubleshooting
403 Forbidden when you trigger a pipeline with a webhook
When you trigger a pipeline with a webhook, the API might return a {"message":"403 Forbidden"} response.
To avoid trigger loops, do not use pipeline events to trigger pipelines.
404 Not Found when triggering a pipeline
A response of {"message":"404 Not Found"} when triggering a pipeline might be caused
by using a personal access token
instead of a pipeline trigger token. Create a new trigger token
and use it instead of the personal access token.
The requested URL returned error: 400 when triggering a pipeline
If you attempt to trigger a pipeline by using a ref that is a branch name that
doesn't exist, GitLab returns The requested URL returned error: 400.
For example, you might accidentally use main for the branch name in a project that
uses a different branch name for its default branch.
Another possible cause for this error is a rule that prevents creation of the pipelines when CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE value is trigger, such as:
rules:
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "trigger"
when: neverReview your workflow:rules to ensure a pipeline can be created when CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE value is trigger.