Deployment approvals (PREMIUM ALL)
- Introduced in GitLab 14.7 with a flag named
deployment_approvals. Disabled by default.- Feature flag removed in GitLab 14.8.
It may be useful to require additional approvals before deploying to certain protected environments (for example, production). This pre-deployment approval requirement is useful to accommodate testing, security, or compliance processes that must happen before each deployment.
When a protected environment requires one or more approvals, all deployments to that environment become blocked and wait for the required approvals from the Allowed to Deploy list before running.
NOTE: See the epic for planned features.
Prerequisites
- Basic knowledge of GitLab Environments and Deployments.
- Basic knowledge of Protected Environments.
Configure deployment approvals for a project
To configure deployment approvals for a project:
Create a deployment job
Create a deployment job in the .gitlab-ci.yml file of the desired project. The job does not need to be manual (when: manual).
Example:
stages:
- deploy
production:
stage: deploy
script:
- 'echo "Deploying to ${CI_ENVIRONMENT_NAME}"'
environment:
name: ${CI_JOB_NAME}Require approvals for a protected environment
There are two ways to configure the approval requirements:
- Unified approval setting ... You can define who can execute and approve deployments. This is useful when there is no separation of duties between executors and approvers in your organization.
- Multiple approval rules ... You can define who can execute or approve deployments. This is useful when there is a separation of duties between executors and approvers in your organization.
NOTE: Multiple approval rules is a more flexible option than the unified approval setting, thus both configurations shouldn't co-exist and multiple approval rules takes the precedence over the unified approval setting if it happens.
Unified approval setting (deprecated)
- UI configuration removed in GitLab 15.11.
WARNING: This feature was deprecated in GitLab 16.1 and is planned for removal in 17.0. Use multiple approval rules instead. This change is a breaking change.
To configure approvals for a protected environment:
- Using the REST API,
set the
required_approval_countfield to 1 or more.
After this is configured, all jobs deploying to this environment automatically go into a blocked state and wait for approvals before running. Ensure that the number of required approvals is less than the number of users allowed to deploy.
Example:
curl --header 'Content-Type: application/json' --request POST \
--data '{"name": "production", "deploy_access_levels": [{"group_id": 9899826}], "required_approval_count": 1}' \
--header "PRIVATE-TOKEN: <your_access_token>" \
"https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/projects/22034114/protected_environments"NOTE: To protect, update, or unprotect an environment, you must have at least the Maintainer role.
Multiple approval rules
- Introduced in GitLab 14.10 with a flag named
deployment_approval_rules. Disabled by default.- Generally available in GitLab 15.0. Feature flag
deployment_approval_rulesremoved.- UI configuration introduced in GitLab 15.11.
- Using the REST API.
-
deploy_access_levelsrepresents which entity can execute the deployment job. -
approval_rulesrepresents which entity can approve the deployment job.
-
- Using the UI.
- Allowed to deploy sets which entities can execute the deployment job.
- Approvers sets which entities can approve the deployment job.
After this is configured, all jobs deploying to this environment automatically go into a blocked state and wait for approvals before running. Ensure that the number of required approvals is less than the number of users allowed to deploy.
A configuration that uses the REST API might look like:
curl --header 'Content-Type: application/json' --request POST \
--data '{"name": "production", "deploy_access_levels": [{"group_id": 138}], "approval_rules": [{"group_id": 134}, {"group_id": 135, "required_approvals": 2}]}' \
--header "PRIVATE-TOKEN: <your_access_token>" \
"https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/groups/128/protected_environments"With this setup:
- The operator group (
group_id: 138) has permission to execute the deployment jobs to theproductionenvironment in the organization (group_id: 128). - The QA tester group (
group_id: 134) and security group (group_id: 135) have permission to approve the deployment jobs to theproductionenvironment in the organization (group_id: 128). - Unless two approvals from security group and one approval from QA tester group have been collected, the operator group can't execute the deployment jobs.
NOTE: To protect, update, or unprotect an environment, you must have at least the Maintainer role.
Migrate to multiple approval rules
You can migrate a protected environment from unified approval rules to multiple approval rules. Unified approval rules allow all entities that can deploy to an environment to approve deployment jobs. To migrate to multiple approval rules, create a new approval rule for each entity allowed to deploy to the environment.
To migrate with the UI:
- On the left sidebar, at the top, select Search GitLab ({search}) to find your project.
- Select Settings > CI/CD.
- Expand Protected environments.
- From the Environment list, select your environment.
- For each entity allowed to deploy to the environment:
- Select Add approval rules.
- In the modal window, select which entity is allowed to approve the deployment job.
- Enter the number of required approvals.
- Select Save.
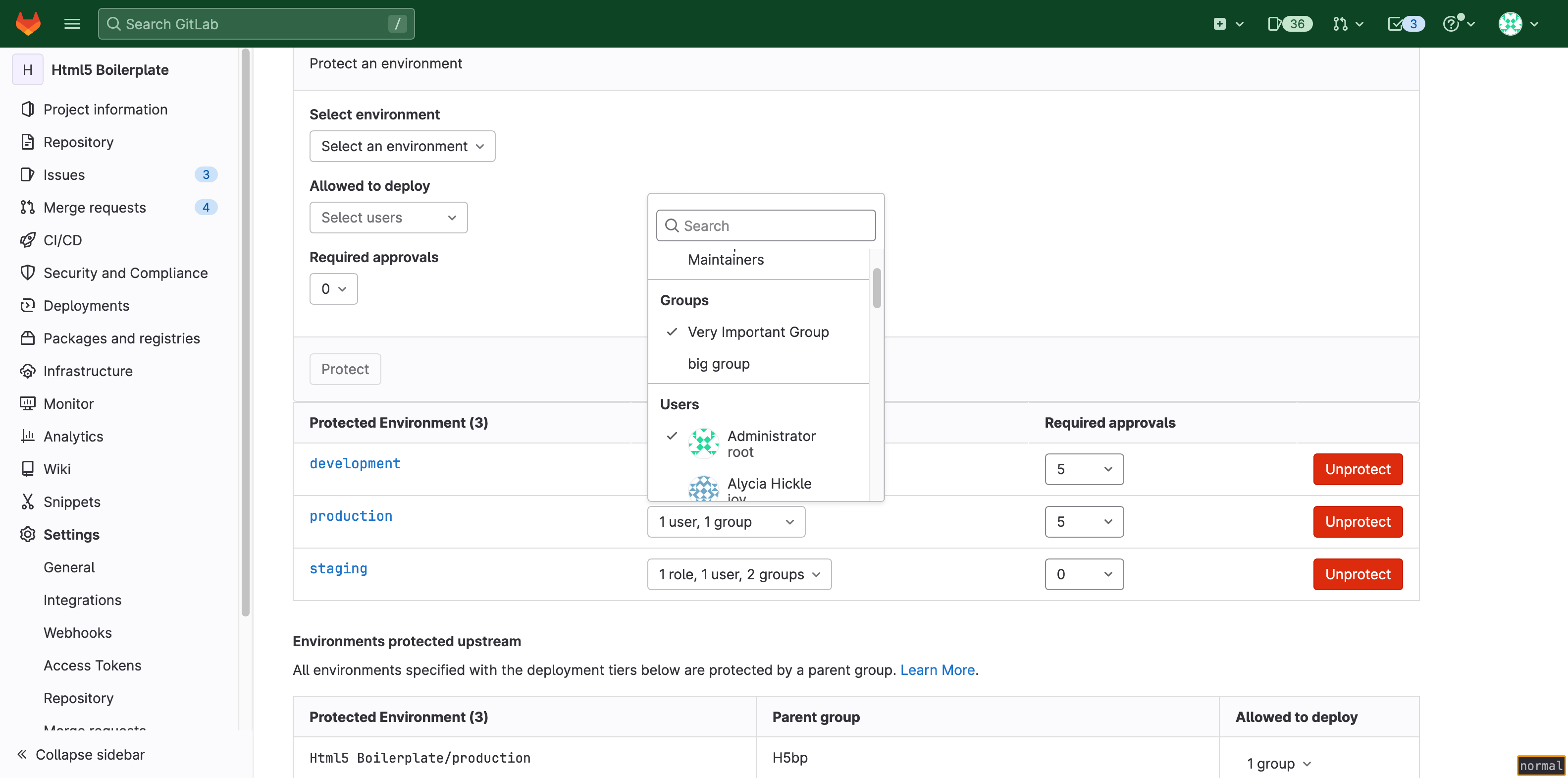
Each deployment requires the specified number of approvals from each entity.
For example, the Production environment below requires five total approvals,
and allows deployments from only the group Very Important Group and the user
Administrator:
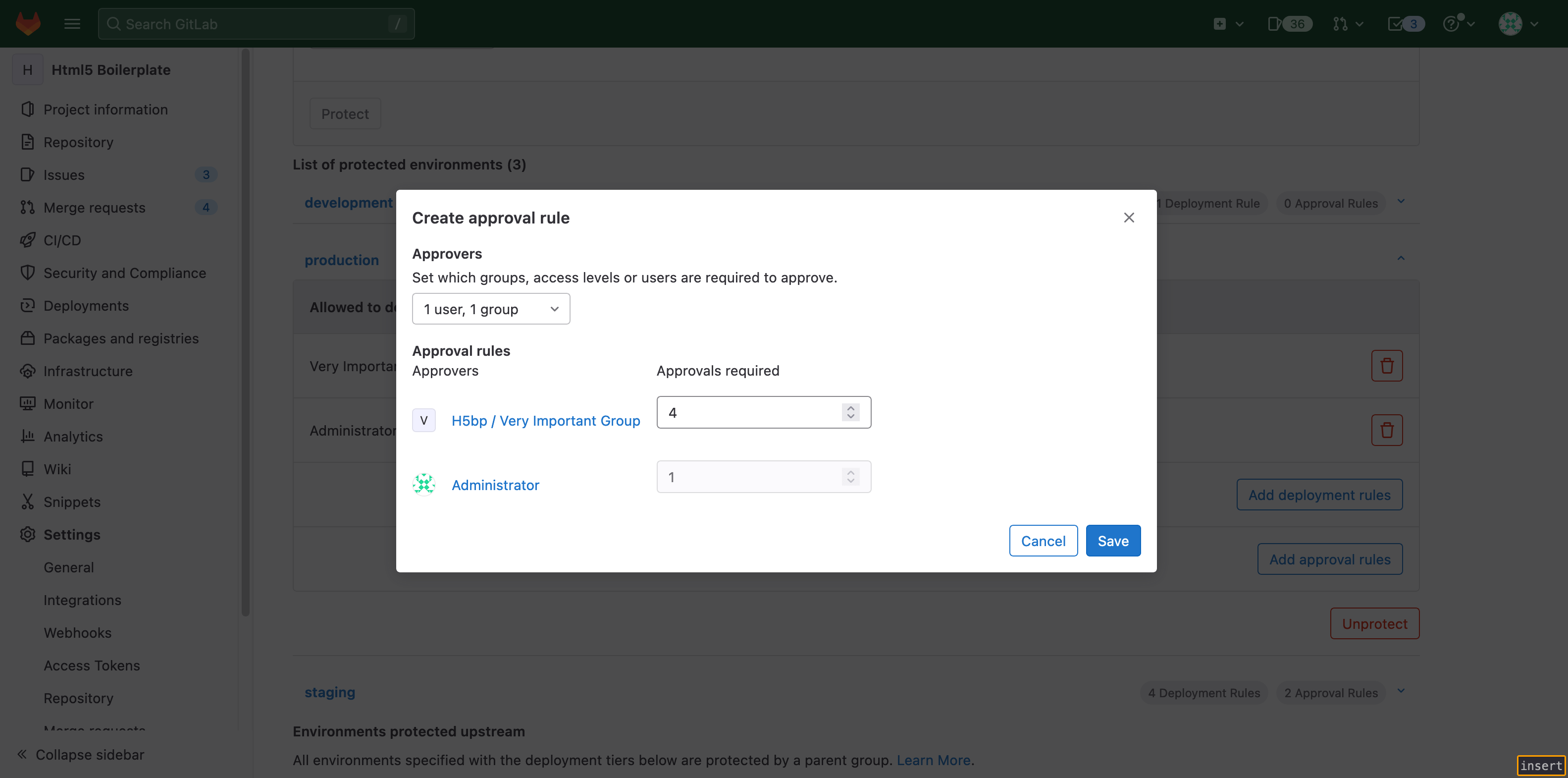
To migrate, create rules for the Very Important Group and Administrator. To
preserve the number of required approvals, set the number of required approvals
for Very Important Group to four and Administrator to one. The new rules
require Administrator to approve every deployment job in Production.
Allow self-approval
- Introduced in GitLab 15.8.
- Automatic approval removed in GitLab 16.2 due to usability issues.
By default, the user who triggers a deployment pipeline can't also approve the deployment job. To allow self-approval of a deployment job:
- On the left sidebar, at the top, select Search GitLab ({search}) to find your project.
- Select Settings > CI/CD.
- Expand Protected environments.
- From the Approval options, select the Allow pipeline triggerer to approve deployment checkbox.
Approve or reject a deployment
Introduced in GitLab 14.9
Using either the GitLab UI or the API, you can:
- Approve a deployment to allow it to proceed.
- Reject a deployment to prevent it.
NOTE: GitLab administrators can approve or reject all deployments.
Approve or reject a deployment using the UI
Prerequisites:
- Permission to deploy to the protected environment.
To approve or reject a deployment to a protected environment using the UI:
- On the left sidebar, at the top, select Search GitLab ({search}) to find your project.
- Select Operate > Environments.
- Select the environment's name.
- In the deployment's row, select Approval options ({thumb-up}). Before approving or rejecting the deployment, you can view the number of approvals granted and remaining, also who has approved or rejected it.
- Optional. Add a comment which describes your reason for approving or rejecting the deployment.
- Select Approve or Reject.
Approve or reject a deployment using the API
Prerequisites:
- Permission to deploy to the protected environment.
To approve or reject a deployment to a protected environment using the API, pass the required attributes. For more details, see Approve or reject a blocked deployment.
Example:
curl --data "status=approved&comment=Looks good to me" \
--header "PRIVATE-TOKEN: <your_access_token>" "https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/projects/1/deployments/1/approval"View the approval details of a deployment
Prerequisites:
- Permission to deploy to the protected environment.
A deployment to a protected environment can only proceed after all required approvals have been granted.
To view the approval details of a deployment:
- On the left sidebar, at the top, select Search GitLab ({search}) to find your project.
- Select Operate > Environments.
- Select the environment's name.
- In the deployment's row, select Approval options ({thumb-up}).
The approval status details are shown:
- Eligible approvers
- Number of approvals granted, and number of approvals required
- Users who have granted approval
- History of approvals or rejections
How to see blocked deployments
Using the UI
- On the left sidebar, at the top, select Search GitLab ({search}) to find your project.
- Select Operate > Environments.
- Select the environment being deployed to.
- Look for the
blockedlabel.
Using the API
Use the Deployments API to see deployments.
- The
statusfield indicates if a deployment is blocked. - When the unified approval setting is configured:
- The
pending_approval_countfield indicates how many approvals are remaining to run a deployment. - The
approvalsfield contains the deployment's approvals.
- The
- When the multiple approval rules is configured:
- The
approval_summaryfield contains the current approval status per rule.
- The
Related features
For details about other GitLab features aimed at protecting deployments, see safe deployments.